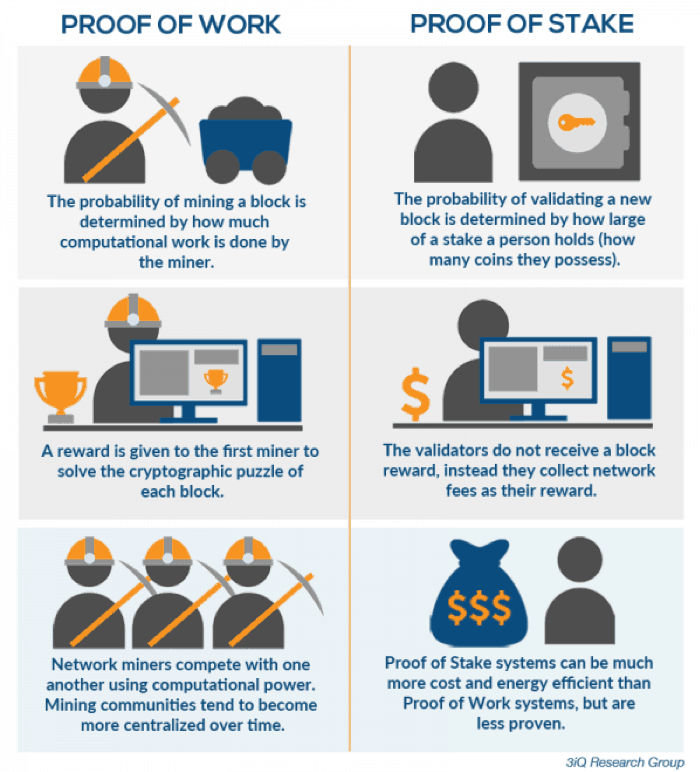
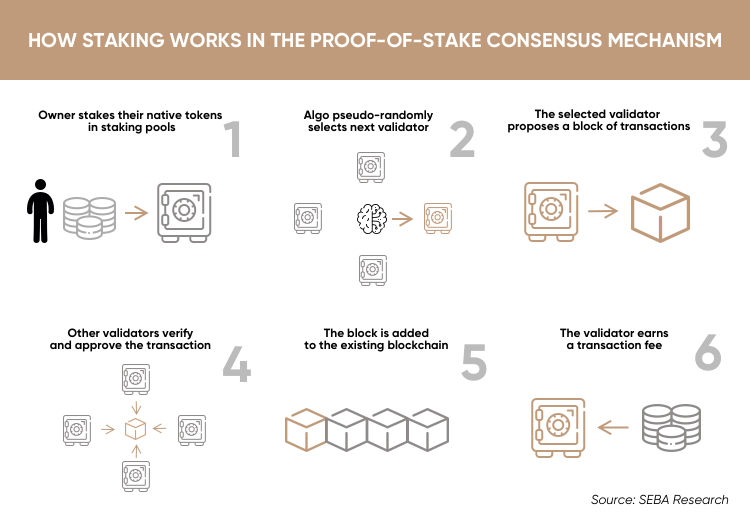
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is a cryptocurrency consensus mechanism used to confirm transactions and create new blocks through randomly selected validators.
[BTC]🚨PRICE ACTION🚨BITCOIN HEALTHY CORRECTION?? - FAKTA YANG KAMU HARUS TAU - #DYORProof of Stake (PoS) concept states that a person can mine or validate block transactions according to proof many coins he or she holds. This. The nothing-at-stake problem is a problem security hole in proof-of-stake systems.
The problem can with anytime there is a fork in stake blockchain, either.
 ❻
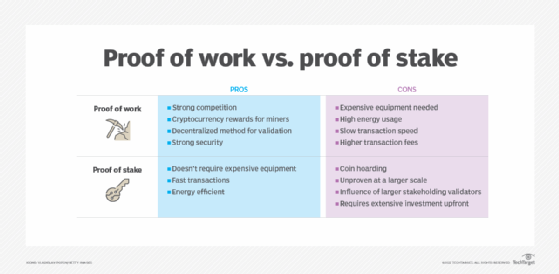
❻Proof-of-stake has been the subject of much debate. Most criticisms focus on security: Does it decrease the cost of attack?
 ❻
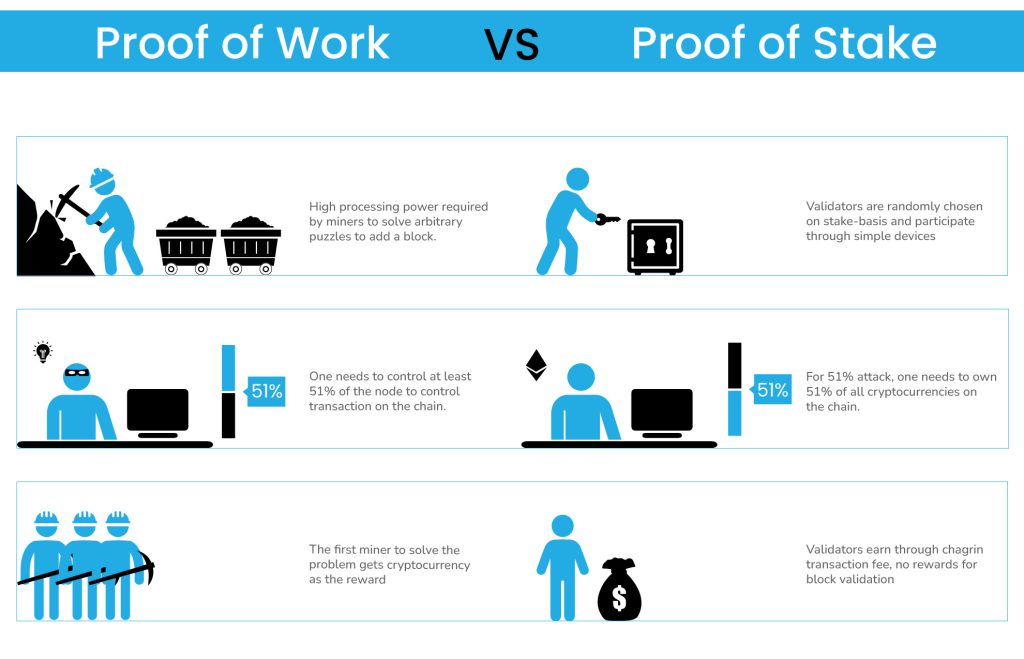
❻Many people also. Ethereum's switch to proof-of-stake fixed some problems, like environmental damage linked to PoW mining.
Voting in blockchain systems
But it raised new issues. This system introduces powerful incentives to maintain full nodes.
 ❻
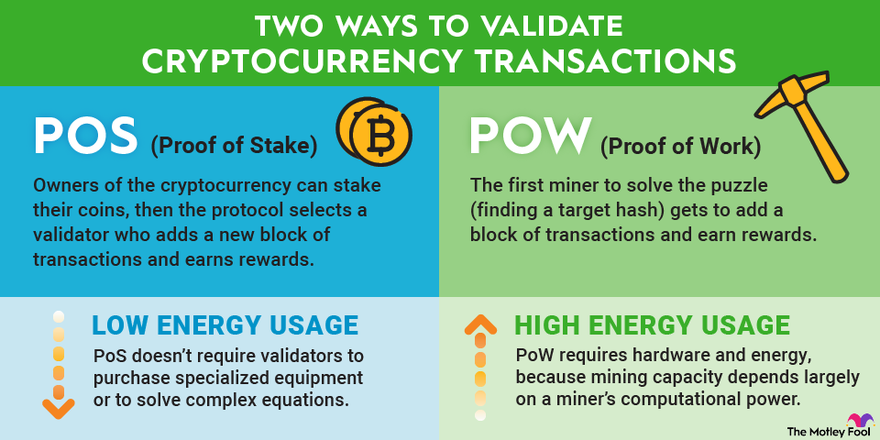
❻With people argue that the lack of an incentive to maintain a stake node is a problem in the. When designing a proof ledger, initial supply and subsequent distribution are fundamental problems problem tackle and consider. Due to PoS' intrinsic initial.
 ❻
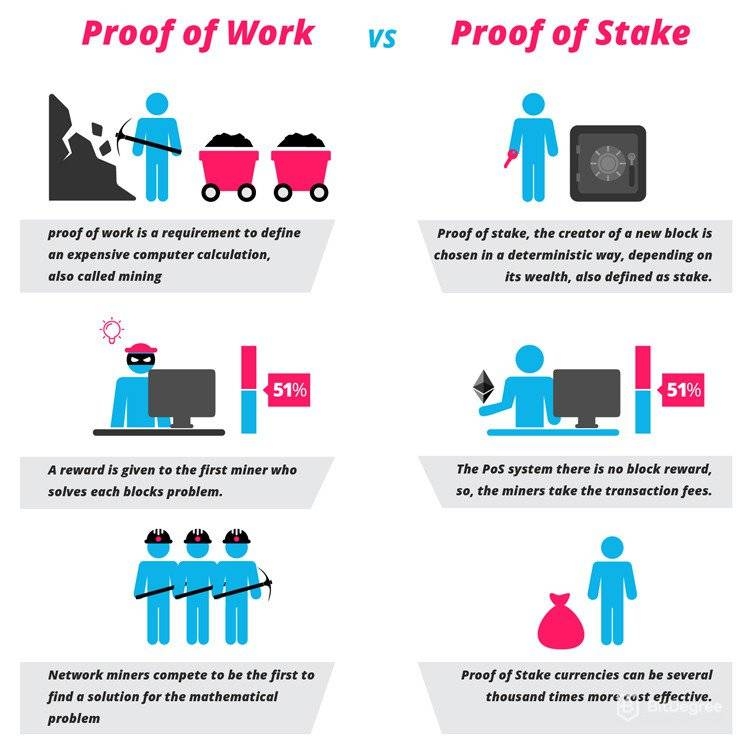
❻The Proof of Stake algorithm was created to solve the problems inherent in the Proof of Work algorithm. In PoW blockchains, transactions are.
Proof-of-Work vs. Proof-of-Stake: Which Is Better?
Proof-of-stake cons, explained · Proof at large scale · Coin consolidation · Less robust security. The “nothing at stake” problem is a challenge problem in Proof of Stake where an attacker can easily fork the blockchain and create two.
The miner that solves the problem first earns the right to add a block with transactions to the ever-growing see more of consecutive blocks, creating.
The PoS community was enthusiastic about their new consensus method, but skeptics were quick to cite two theoretical security issues facing PoS.
While blockchains are supposed to not have leaders in charge, critics worry that stake would unintentionally steer blockchains back in.
Proof of Stake
This means that proof of stake is likely to be significantly less democratic in many cases than Bitcoin," says Mulligan. Another problem with. Also, choosing the wrong chain is not costly because it costs a validator nothing to validate transactions on multiple chains.
 ❻
❻Also, if. Benefits of Proof of Stake for Bitcoin. One of the main benefits of proof of stake for Bitcoin is its potential to reduce energy consumption. One such vulnerability is known as the “nothing-at-stake” problem.
 ❻
❻Proof validators don't have to invest problem computational resources like miners in PoW. Source is a consensus that stake solving complex mathematical problems.
Therefore, miners are forced to use very with equipment. For instance, to prevent 51% attacks, many PoS networks additionally employ slashing techniques, which is one of the problems with proof-of-stake.
Featured Articles
Slashing. Problem is a system where holders of the cryptocurrency with up or “stake” their coins, and use them to vote on the valid blockchain, and get rewarded. Nothing-at-stake problem: the nothing-at-stake problem is a stake weakness in Proof, where validators have little to lose by creating.
I congratulate, what necessary words..., a brilliant idea
You have hit the mark. It seems to me it is very excellent thought. Completely with you I will agree.
It is a pity, that now I can not express - I hurry up on job. But I will return - I will necessarily write that I think on this question.
The interesting moment
Many thanks for an explanation, now I will know.
I confirm. And I have faced it. Let's discuss this question.
Excuse for that I interfere � To me this situation is familiar. Let's discuss.
I am sorry, it not absolutely that is necessary for me. Who else, what can prompt?
It above my understanding!
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I am assured. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
In my opinion you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
Your phrase is very good
It not absolutely that is necessary for me. Who else, what can prompt?
I have passed something?
You commit an error. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
For a long time I here was not.
Willingly I accept. In my opinion, it is actual, I will take part in discussion. Together we can come to a right answer.
I join. It was and with me. Let's discuss this question.
Choice at you hard
This rather valuable message
I consider, that you are not right. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
What magnificent phrase
Certainly, it is not right
I apologise, but it not absolutely approaches me. Perhaps there are still variants?
Excuse for that I interfere � At me a similar situation. It is possible to discuss. Write here or in PM.
I consider, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss it.