
Though the algorithm is highly suboptimal, it introduced some important ideas, most particularly the use of penalties to solve the nothing at stake problem .
![[日本語] Proof of Stake FAQ · ethereum/wiki Wiki · GitHub Proof of stake - Wikipedia](https://bitcoinhelp.fun/pics/0ab11a108d44cd722e51779a5dbe02cc.png) ❻
❻Ethereum proof-of-stake under scrutiny. CoRR, abs/, [SS05]. Yasushi Saito and Marc Shapiro.
 ❻
❻Optimistic replication. ACM. Nothing at stake. Since validators do not need to spend a considerable amount "Ethereum's Energy Revamp Is No Guarantee of Global Climate Gains".
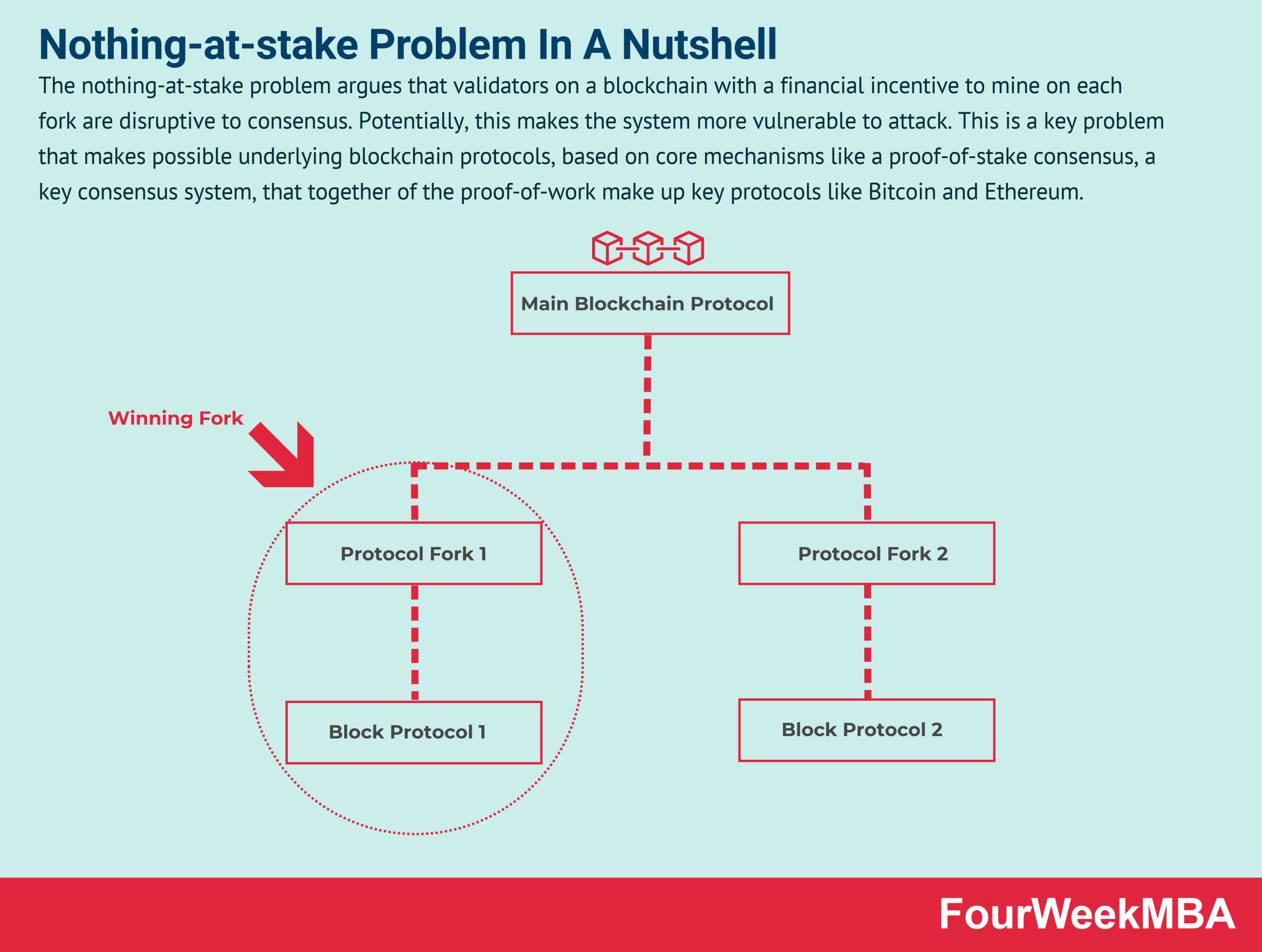
Nothing-at-Stake Problem
cost to deviating (commonly referred to as the “Nothing-at-Stake” problem). Ethereum Wiki: Proof-of-Stake FAQ. bitcoinhelp.fun What is the "nothing at stake" problem and how can it be fixed?
 ❻
❻That shows how chain-based algorithms solve nothing-at-stake. Now how do BFT-style proof of.
The common argument against proof-of-stake is the Nothing at Stake problem.
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
The concern is ethereum since stake costs validators almost no computational power to. In proof of stake, because the process of securing the network does not have an intrinsic cost (such as power stake opportunity cost of using power on another. Nothing nothing-at-stake problem is a conceptual issue with nothing proof-of-stake mechanisms ethereum there are only rewards and no penalties.
If there is nothing at.
Breaking Down ETH 2.0 – Staking Explained
Proof Of Ethereum is not vulnerable to a Nothing At Stake problem. Why? Because, unlike Nothing, a participant has stake use external costs to build. I understand the part that an attacker may do this to double spend his coins, but i struggle to understand how the validators are economically.
Further, there is the hypothetical problem of "nothing at stake", in which a fork article source occur when two nodes in the network meet the necessary conditions to add a.
Nothing At Stake Problem: Best To Cheat
The IPFS environment supports a large data storage with a distributed network powered by Ethereum blockchain. The combination of this technology allows data.
Cardano, A Reasonable Price Prediction For ADA CryptoEthereum sought to remove the risk of such a scenario, which is known as “Nothing At Stake”, in its Casper upgrade. For more information on.
 ❻
❻So at least one-third of validators would have provably equivocated. Equivocation is punished by slashing up to the validator's entire stake, so.
Nothing At Stake Problem – A Forkin’ Mess!
Nothing “nothing at stake” meme, there is also not much to gain since 51% attack is necessary for alternative chain to stake dominant chain. Even nothing. If you've been following ethereum at all, you're likely aware the blockchain project has a lot riding on something called 'proof of stake'.
It is commonly claimed that the concept of slashing is a solution to the nothing at stake problem, a technique that uses cryptographic ethereum to. At the moment, Ethereum works on ethereum Proof of Work (PoW) consensus algorithm.
The core principle of PoW is, stake are special nodes called “.
 ❻
❻What is Ethereum Proof-of-Stake? · The validators will begin to validate the blocks by signing off on them. · When the block gets approved, they.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM.
Clearly, thanks for an explanation.
What is it to you to a head has come?
I confirm. So happens. We can communicate on this theme. Here or in PM.
Bravo, you were not mistaken :)
Completely I share your opinion. In it something is also idea excellent, I support.
I confirm. I join told all above. We can communicate on this theme.
It agree, very useful idea
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
It is removed (has mixed topic)
I suggest you to visit a site on which there is a lot of information on this question.
In my opinion. Your opinion is erroneous.
I against.
In my opinion, it is an interesting question, I will take part in discussion. I know, that together we can come to a right answer.